6 Types of Injection Molding Materials for Product Projects
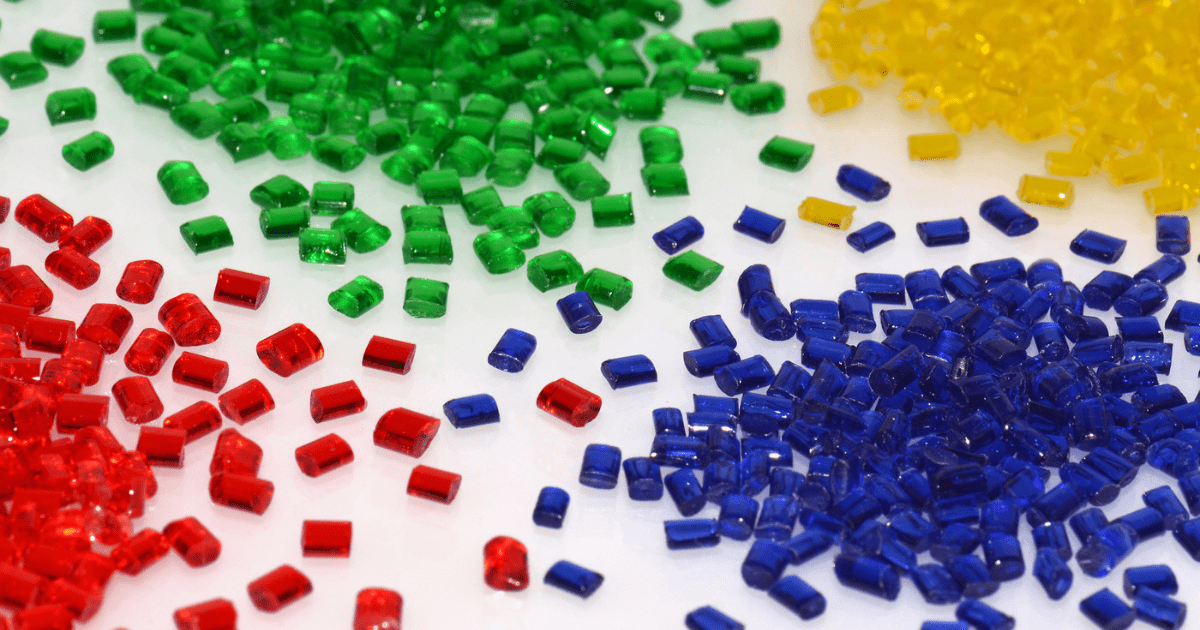

Choosing the right injection molding materials is of high importance as it will determine the quality and reliability of the mold, an essential part of the development phase of a project.
The Main Characteristics of Injection Molding Materials
There are a lot of different injection molding materials that can be used in mold development. Even though they might vary in some aspects, there are some main characteristics that are common to all of them:
- All injection molding materials are made with thermoplastic, a type of plastic that can be molded when exposed to high temperatures.
- To be manipulated with temperature, these materials need heat from 135°C to 250°C to be worked with, depending on the type.
- After being exposed to heat and molded, injection molding materials can be cooled or hardened at room temperature.
- Once they’re settled, they have great thermic stability, meaning these materials are resistant to breaking down with heat (in other words: melt).
- Injection molding materials can be recycled and reused, with limitations of course.
All the types of injection molding materials have these specifications as a base and vary in other features.
Types of Molding Materials
As mentioned, there are various types of injection molding materials, but there are a few of them that are more common, such as:
- Polycarbonate (PC): It’s a strong, lightweight, and highly transparent material. PC is stronger than glass and durable while offering some flexibility (but not a lot compared to other injection molding materials).
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): ABS is a material that can be molded at a relatively low melting point, making it easier to work with. It has good finishes with high impact resistance but lacks resistance to external weather conditions and friction.
- Nylon Polyamide (PA): This injection molding material is highly resistant to breakage, impact, fatigue and heat. Even though nylon is not necessarily flame and UV resistant, there are some versions of this material with different types of fibers that do. It needs high temperatures to be molded.
- Polyoxymethylene (POM): Also known as acetal, POM has great rigidity and elasticity, meaning it can hold its original shape while giving flexibility, without damage. It’s resistant to abrasion, breakage and has low water absorption. POM is also known for its good finishes.
- Polypropylene (PP): This material is one of the most used plastics in daily utensils. It usually has a low cost, while being able to provide high breakage and impact resistance. PP also has low humidity absorption and is easy to color and mold.
- Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE): TPE is a blend of plastic and rubber materials, making it have a rubbery touch. With this, this injection molding material has great adherence, flexibility and impact resistance.
These materials can generally be colored. Besides their properties, you can add to them UV protection additives, flame resistance additives, glass fibers for glass-looking finishes, and carbon fibers to acquire resistance.
Some of these injection molding materials can also be mixed to combine their features. For example, you can combine PC and ABS.
-min.png?width=1200&height=630&name=New%20Project%20(26)-min.png)
How to Choose the Best Molding Materials
There is no obvious way to choose the right injection molding material. It always depends on what the specifications your project has and needs.
In this decision you need to consider factors such as budget, what type of finish is desired (rubbery, glass-looking, sturdy, etc.), what characteristics are needed (types of resistance, flexibility, etc.), and so on.
This choice is part of the process of developing a product and needs to be made accordingly to such.
What Materials does Yelco use?
Yelco develops their molds with different types of injection molding materials. The choice of injection molding materials always depends on the necessities of the specific project, but overall, the most used materials in our telco projects are:
- ABS for indoor products and components that aren’t meant to be exposed to the weather.
- PP, ASA, and PA for the exterior of products (like covers), and outdoor products.
- POM, usually for interior pieces and pieces that require flexibility.
- TPE to simulate rubber.
You can learn more about Yelco’s product development process in the following article: Telecom Products Customization: What it is and How to Improve your Products