What is GPON and How Does It Work?

If you are reading this blog, it is because you are interested in the topics that we cover here, and you are connected to the world of telecommunications.
The current world trend, in terms of telecommunications, is to have “everything connected, always connected”, in which there is a need for a continuous connection to the internet, and with more and more devices. Consequently, the volumes of information are massive, which makes network security a critical matter. In addition to all this, the concern with sustainability and the reduction of energy consumption is a necessity to bear in mind.
GPON networks can be a great advantage and fill these current needs.
What is GPON?
A GPON network is a purely passive fiber optic network that allows the transmission of large amounts of information between a central point and several distributed points, up to a radius of 20 km from that central point.
GPON is an acronym that stands for Gibabit Passive Optical Network, and as the name implies, it is an optical, passive network that works in the order of Gigabits per second.
When we talk about bits per second, we are talking about the amount of information that is transmitted in a network, per unit of time. This quantity is commonly called “bandwidth”.
How does it work?
As we have already had the opportunity to present in previous articles, a PON network comprises the existence of an equipment at a central point, called OLT, which will communicate with other equipment, called ONT's, installed next to the end user, through a fiber optic network. Each OLT port can manage up to 64 ONTs, and this division occurs in the passive network, through the use of optical splitters.
Transmission protocols in Telecommunications networks are defined by the ITU-T recommendations and define, among several parameters, the transmission speeds for each type of network.
The ITU-T recommendation G.984 defines that the transmission speed, in the GPON protocol, is 2.5 GBps (Gibabit per second) in Downstream, and 1.25 GBps in Upstream.
When we talk about bandwidths of this magnitude, we are talking about broadband networks, which offer their users great data transmission capacities, which allows to meet the current bandwidth needs of most of the users.
All transmission in GPON is done through a single optical path, between the OLT and the ONT, using two different wavelengths: 1490nm for Downstream transmission; 1310nm for Upstream transmission.
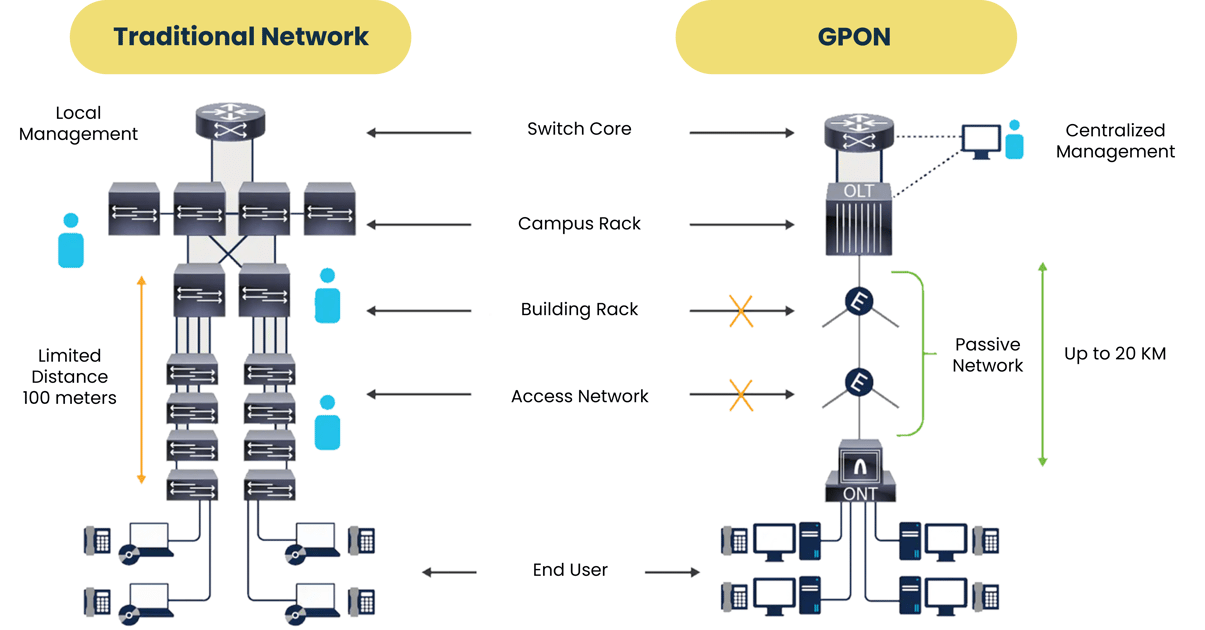
Traditional Network VS GPON
Downstream Transmission
In Downstream, where we have a fiber leaving the OLT, that will be divided by several ONT's, the data is packaged and addressed, and is distributed in "broadcast", with each ONT only collecting what is properly addressed to it.
Upstream transmission
In Upstream, where we have several ONTs forwarding the data to a single fiber in the OLT, the data transmission is done by time slots, in which each ONT sends information in its defined time slot.
Currently, there are technological evolutions that allow the evolution of GPON to protocols with greater bandwidth, such as XG-PON, NG-PON2 and the latest protocol XGS-PON that establishes the transmission of 10GBps in both directions!
What are its main benefits?
Compared to traditional networks, whether metropolitan operator access networks or local access networks, GPON networks have numerous advantages, of which I will highlight a few:
Bandwidth - Large data transmission capacities, where the installed fiber network has a lifespan of more than 25 years. With the technological evolution, to update a GPON network, it is enough to change the equipment at the ends, without the need to change the passive fiber optic network.
Sustainability – GPON networks use much less equipment than a traditional network, so their energy consumption is drastically reduced. Less transmission equipment translates into less accessory equipment: AC's, security, etc.
Cost Reduction - less equipment used and with a low maintenance passive fiber optic network, the costs of GPON networks decrease dramatically, both in terms of CAPEX and OPEX
Where can it be used?
GPON networks are used more and more by more operators globally, to reach their customers with telecommunication services. Broadband networks are allowing the creation of a new paradigm and are leading to the digital transformation, not only of companies or cities but of entire nations. With broadband networks, an entire digital ecosystem can be created that will allow changes in behavior and reduction of resources, such as:
Remote work – no need to commute, allowing more time for other activities.
Remote health services – reduced travel and faster service.
Online government services – reduction of bureaucracy in public services and faster services.
GPON networks can also be applied as local access networks (LANs), where copper networks currently predominate.
These can be applied to:
- Companies with many workstations or connection points (sensors, machine control, etc.)
- university campuses
- big factories
- Industrial zones and parks
- sports complexes
- city councils
Optical fibers are here to stay and telecommunications are increasingly demanding. GPON networks certainly make a very important contribution to the worldwide technological development and to the digital transformation that is so much talked about.


