Difference between Patent and Utility Model: Know how to Protect your Products

In every industrial sector or field, we can find people with creative minds, capable of inventing new ideas, products, processes, and so on, that can be applied to their industry. To protect these original concepts, it’s fundamental to implement a patent or a utility model.
What is a Patent?
A patent is essentially a contract made between the creator or company of an original solution for a specific problem in the industry, and the state of a country. These are implemented to protect the creation and exploration rights of such solutions, so they can’t be claimed by someone else.
To get a patent, there is a process a creator must go through. This process starts by them submitting a request for the patent, which will then be examined. If the product or process passes the examination stage, the patent is granted.
There are three fundamental characteristics that a concept must have to get a patent:
- It has to be completely new, not something that was already present in the respective industry;
- The product or process shall come out of inventive activity, a creative process with the aim of getting an innovative solution;
- Lastly, it must be applicable to the industry, reliable, and functioning, to have its value proven.
A patent is valid for 20 years, that start at the moment of the request. During that time, such original products and processes, as well as their use, are protected by law. This means no other person or company, except the creator, can claim, manufacture and/or commercialize the same concept.
What is an Utility Model?
A utility model can be implemented to protect an invention, similarly to a patent. This grants the exclusive commercial rights of an invention to the creator, protecting such from being claimed and explored by someone else.
To be granted a utility model, the concept must have some local innovative value for the industry, but the requirements for examination are optional.
This protection can’t be applied to biological inventions, chemical processes, pharmaceutical drugs and substances.
Utility models’ validity time varies from one country to another, but independently of the location, it starts on the date of the request.
What is the difference between a Patent and a Utility Model?
There are some key differences between a utility model and a patent:
- Firstly, a patent usually protects an invention for more time than a utility model, granting the rights for commercializing it longer.
- Requirements-wise, a utility model has a simpler acceptance process that is less strict than the one for a patent.
- Having a simpler process, a utility model can be granted to minor inventions that don’t necessarily qualify for a patent but still have local innovative value.
How does the process of protecting a product Work?
As mentioned before, there are a few steps for getting a product protected: registering for it, examination of the request, and getting it granted.
Before putting in a request for the protection of an invention, there are some steps you can take in advance:
- To make sure your protection request passes the examination phase, it’s important that you check how the state of the industry is, to make sure there’s no other invention like yours available to the public already.
- You should also work on writing a description of your concept, following legal requirements, to submit with your registration for protection.
Yelco’s products protected by Patents and Utility Models
Being a creative company, Yelco works daily to develop innovative products to solve the telecom industry's problems.
To protect our inventions, some of our products have been granted patents and utility models. These are:
- The Advanced Optical Point – Patent in Portugal and in Europe.
 |
-min.png?width=1920&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(1)-min.png) |
- The Clamp for Securing Excess Slack in Aerial Cables – Patent in Portugal and in Europe.
|
|
|
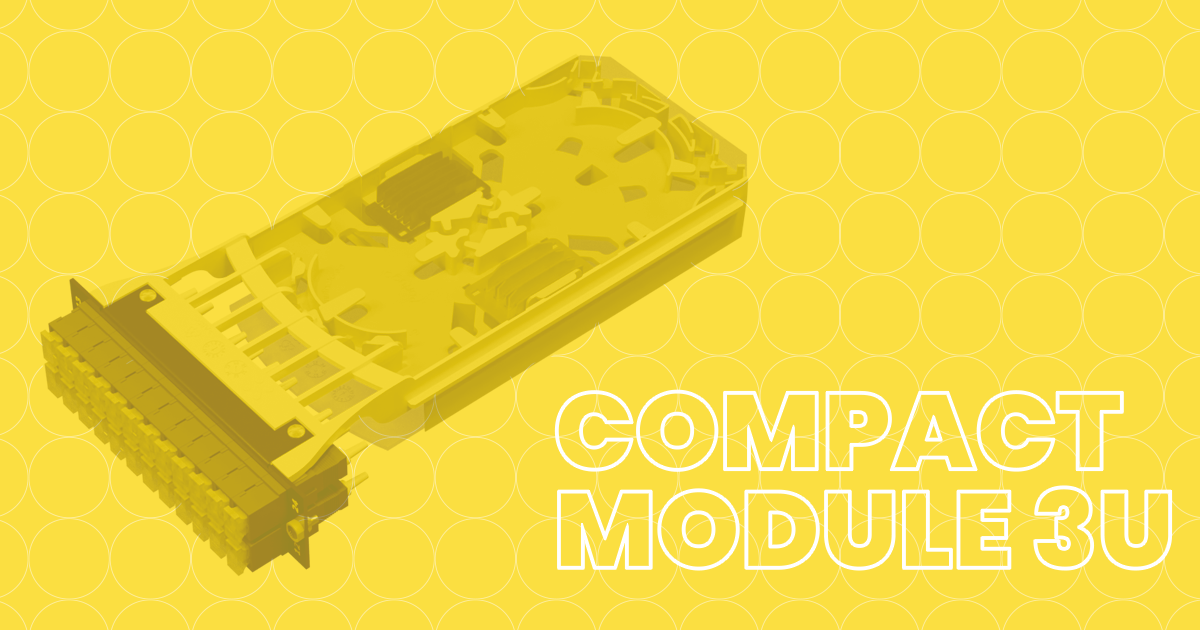
- The Fiberoptic Compact Module 3U for 12 & 24FO – Patent in Portugal.
-min.png?width=1920&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(2)-min.png) |
-min.png?width=2304&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(5)-min.png) |
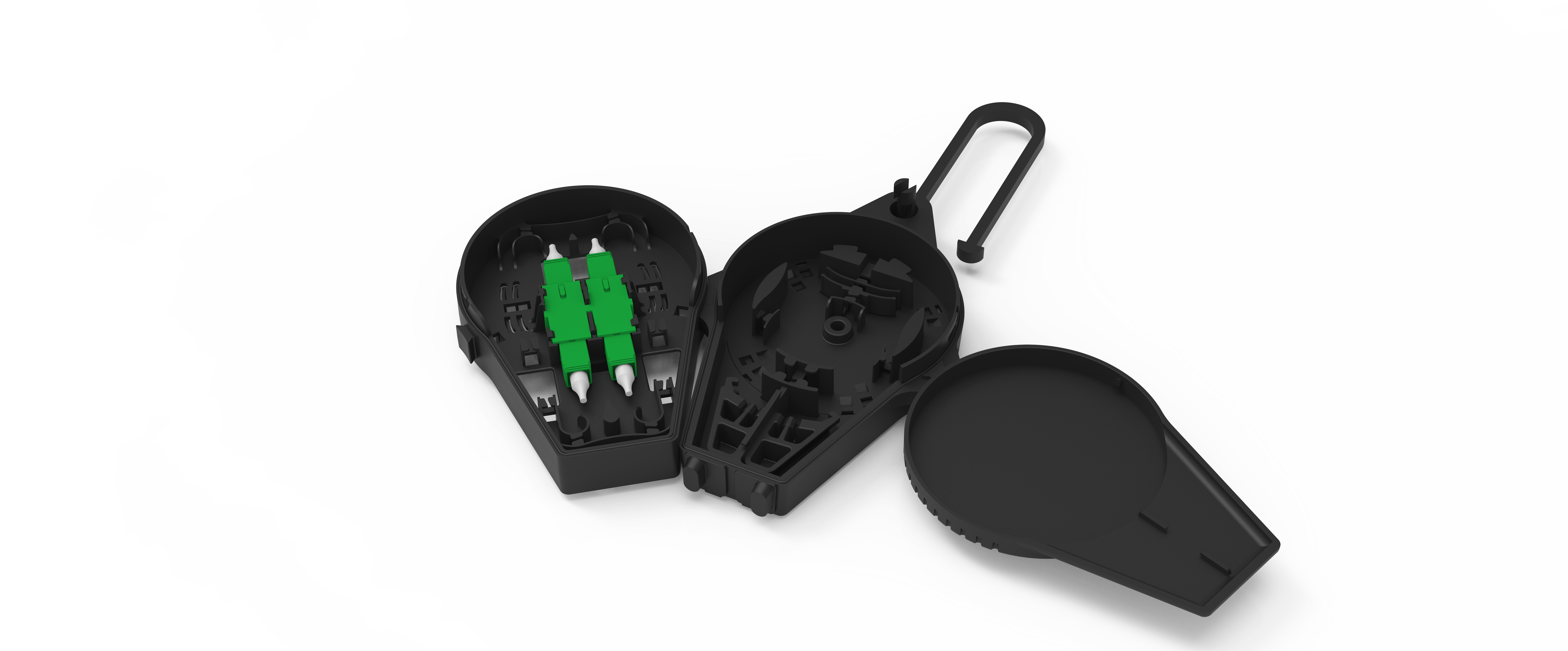
- The Internal Fiber Distribution Enclosed Connectorized & Splice version – Utility Model in Portugal and in Spain.
-min.png?width=7680&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(6)-min.png) |
-min.png?width=7680&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(7)-min.png) |
- The Indoor Multi Dwelling Unit Box for 38 & 72FO – Utility Model in Portugal.
-min.png?width=1920&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(9)-min.png) |
-min.png?width=2496&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(8)-min.png) |

-min.png?width=1920&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(3)-min.png)
-min.png?width=1920&name=MicrosoftTeams-image%20(4)-min.png)