
Injection Molding Materials for Product Development
Choosing the right injection molding materials is critical, as it directly impacts the quality, performance, and durability of a product—especially during the development phase of telecom and industrial components.
The Main Characteristics of Injection Molding Materials
All are thermoplastics, meaning they can be heated and reshaped without altering their fundamental properties.
These materials require heat between 135°C and 250°C to be processed, depending on the type.
After molding, they cool and solidify at room temperature.
Once set, they offer excellent thermal stability and do not degrade easily under heat.
Most are recyclable and can be reused, within certain limits.
These shared traits are foundational, though each material also brings distinct features.
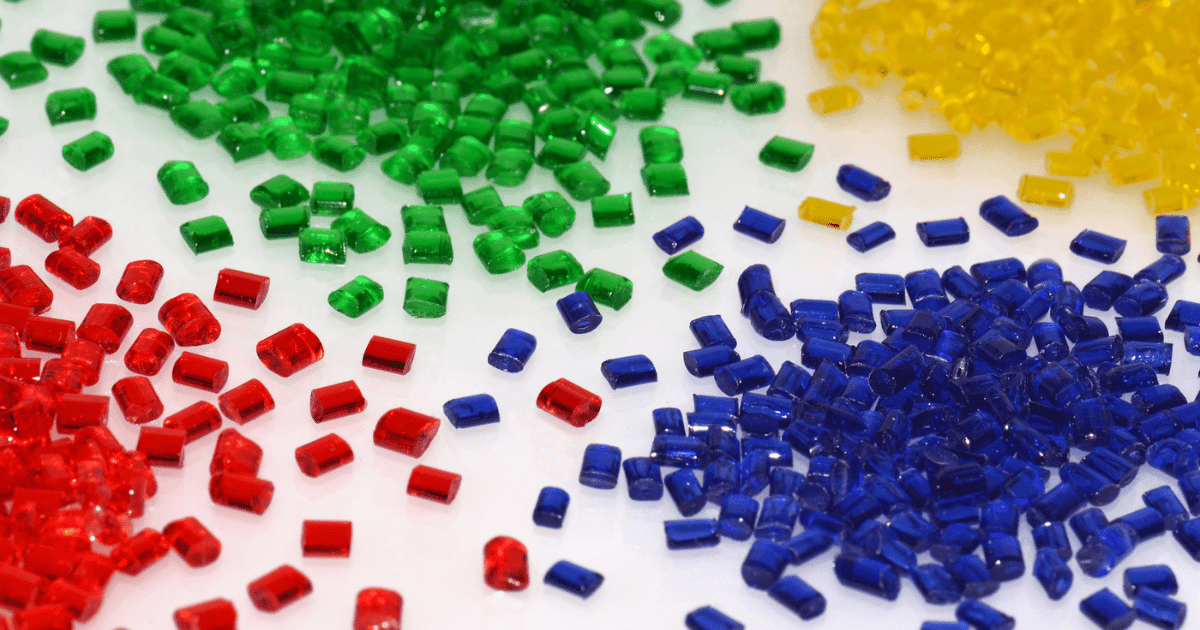
Common Types of Molding Materials
Here are six widely used injection molding materials:
Polycarbonate (PC): Lightweight, highly transparent, and stronger than glass. Offers good impact resistance with limited flexibility.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): Easy to mold at low temperatures and provides good finishes and impact resistance. However, it’s less suitable for outdoor or high-friction environments.
Nylon Polyamide (PA): Offers high resistance to breakage, fatigue, and heat. Some formulations include flame or UV-resistant fibers. It requires high processing temperatures.
Polyoxymethylene (POM): Also called acetal, POM combines rigidity and flexibility. It resists abrasion, maintains shape under stress, and delivers clean finishes.
Polypropylene (PP): Affordable and highly resistant to impact and humidity. Easy to color and mold, making it ideal for various everyday and industrial applications.
Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE): A rubber-plastic blend that feels soft and flexible. It offers excellent grip, flexibility, and impact resistance.
Many of these can be customized with additives such as:
UV protection
Flame resistance
Glass fibers (for aesthetic or structural properties)
Carbon fibers (for increased strength)
Some materials can also be blended—like PC and ABS—to balance different properties.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. The best material depends on your project’s specific needs, including:
Budget
Desired finish (smooth, rubbery, transparent, etc.)
Required resistance (impact, UV, chemical)
Flexibility and structural performance
Choosing the right injection molding material is an essential part of a product’s development and should align with its function, environment, and user expectations.
What Materials Does Yelco Use?
At Yelco, the choice of injection molding materials is tailored to each project’s technical requirements. For our telecom product development, we most frequently use:
ABS for indoor applications where weather exposure is not a concern.
PP, ASA, and PA for outdoor products and exterior parts like protective covers.
POM for internal components requiring flexibility or structural precision.
TPE to simulate rubber for grips, seals, or flexible areas.
Learn more about how we develop customized telecom products in this article: Telecom Products Customization: What it is and How to Improve your Products

Article by

